Understanding African Horse Sickness: A Comprehensive Guide
African horse sickness (AHS) is a viral disease that affects horses, donkeys, and zebras. It is caused by a virus belonging to the genus Orbivirus, which is spread through the bite of infected midges (Culicoides species). The disease is characterized by fever, respiratory distress, and swelling of the head and neck. While it can be fatal, especially in horses, some animals may only experience mild symptoms or remain asymptomatic.
What Animals Does African Horse Sickness Affect?
AHS primarily affects equids, with varying levels of susceptibility and severity among different species.
- Horses: They are the most susceptible to AHS and often experience the most severe symptoms, leading to high mortality rates.
- Donkeys: While donkeys can contract the virus, they are generally more resistant than horses and tend to exhibit milder clinical signs.
- Zebras: As native to Africa, zebras have developed a natural resistance to AHS and often act as carriers without showing significant symptoms.
 Animals Affected by African Horse Sickness
Animals Affected by African Horse Sickness
Symptoms and Transmission of African Horse Sickness
Recognizing the symptoms of AHS is crucial for prompt diagnosis and management. The severity can vary, and some animals may only show mild signs:
- High fever: One of the initial signs is a rapid increase in body temperature.
- Respiratory distress: Difficulty breathing, coughing, and nasal discharge are common symptoms.
- Swelling: The head and neck often exhibit significant swelling, particularly around the eyes and jaw.
- Colic: Some animals may experience abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Cardiac abnormalities: In severe cases, the virus can affect the heart, leading to heart failure.
AHS is not contagious through direct contact between animals. Instead, it spreads primarily through the bite of infected midges, which act as vectors. These insects breed in damp environments such as muddy areas and stagnant water.
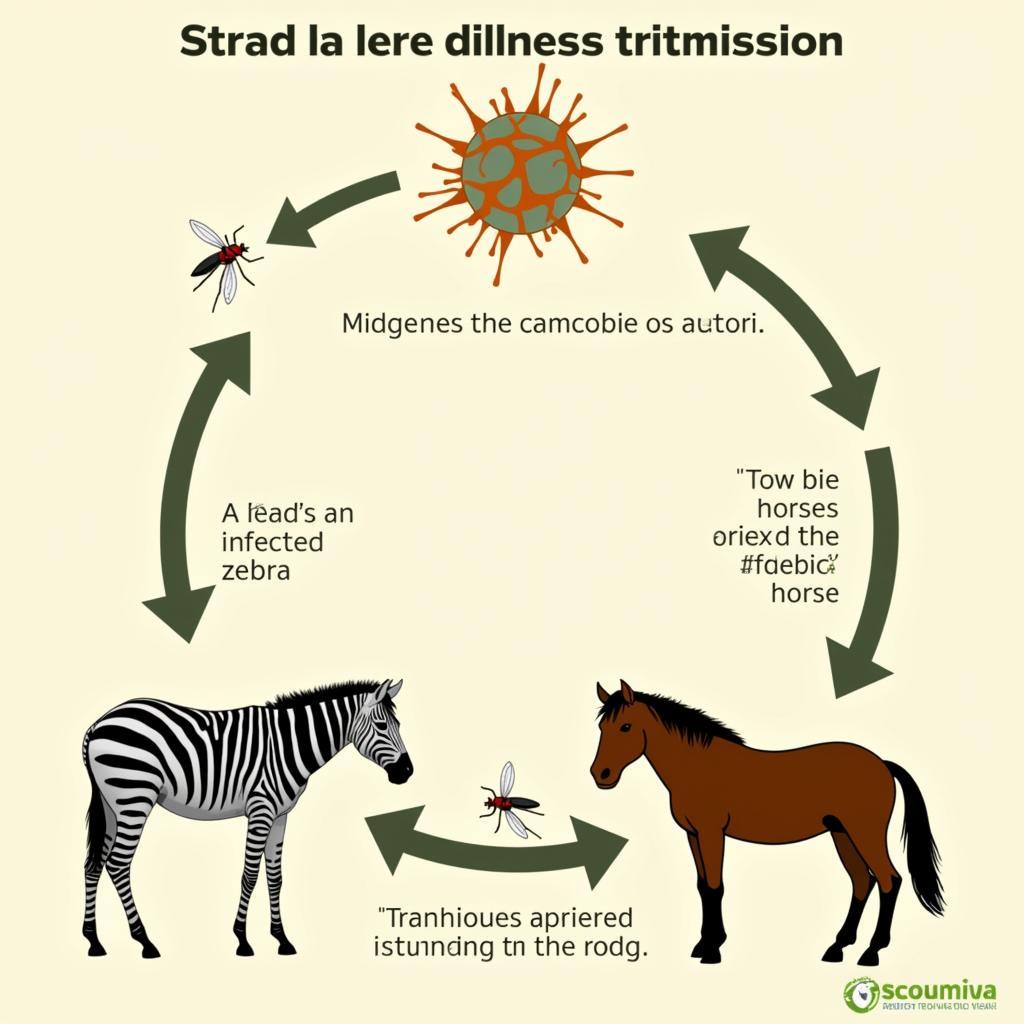 How African Horse Sickness Spreads
How African Horse Sickness Spreads
“Understanding the transmission cycle of African Horse Sickness is vital for implementing effective control measures,” states Dr. Amani Jabari, a veterinarian specializing in equine diseases at the University of Nairobi. “Controlling midge populations through environmental management and insect repellents is crucial in preventing the spread of the virus.”
Diagnosis and Treatment of African Horse Sickness
Early diagnosis is essential for improving the chances of survival, especially in horses. Veterinarians use a combination of clinical signs, blood tests, and post-mortem examinations to confirm the presence of the virus.
Treatment for AHS is primarily supportive, focusing on alleviating symptoms and providing comfort to the affected animal.
- Rest and hydration: Providing a stress-free environment and ensuring adequate water intake is crucial.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce fever and inflammation.
- Oxygen therapy: In cases of severe respiratory distress, oxygen supplementation may be necessary.
While there is no specific cure for AHS, prompt veterinary care can significantly improve the outcome, especially in cases with milder symptoms.
 Preventing African Horse Sickness Outbreaks
Preventing African Horse Sickness Outbreaks
Preventing African Horse Sickness Outbreaks
Prevention plays a paramount role in managing AHS. Implementing effective control measures can help protect equids and limit the spread of the virus.
- Vaccination: Vaccination remains the most effective method for preventing AHS. Several types of vaccines are available, and consulting with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate vaccination protocol for specific regions and risk factors is essential.
- Insect control: Managing midge populations is crucial. This includes eliminating breeding sites by removing standing water, using insecticides, and employing physical barriers such as screens and nets.
- Quarantine measures: Implementing strict quarantine protocols for animals entering areas free of AHS is essential to prevent the introduction of the virus.
- Movement restrictions: During outbreaks, restricting animal movement can help contain the spread of the disease.
“Preventing African Horse Sickness requires a multifaceted approach involving vaccination, vector control, and biosecurity measures,” emphasizes Dr. Jabari. “By working together, horse owners, veterinarians, and authorities can minimize the impact of this devastating disease.”
Conclusion
African Horse Sickness poses a significant threat to equid populations, particularly in Africa. Understanding the disease, its transmission, and prevention strategies is crucial for safeguarding these animals. By implementing comprehensive control measures and seeking veterinary care promptly, we can mitigate the impact of AHS and protect the health and well-being of horses, donkeys, and zebras.
For any concerns regarding African Horse Sickness, seeking immediate veterinary assistance is paramount. You can also contact us at +255768904061, email us at kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit our office located at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to address your queries and provide support.

