African Israelite Tribes: A Journey into Identity and Belief
African Israelite Tribes represent a fascinating and complex tapestry of cultural and religious expression found across the African continent. These communities, often claiming descent from the ancient Israelites, have developed unique traditions and practices that blend elements of Judaism, Christianity, and indigenous African spirituality.
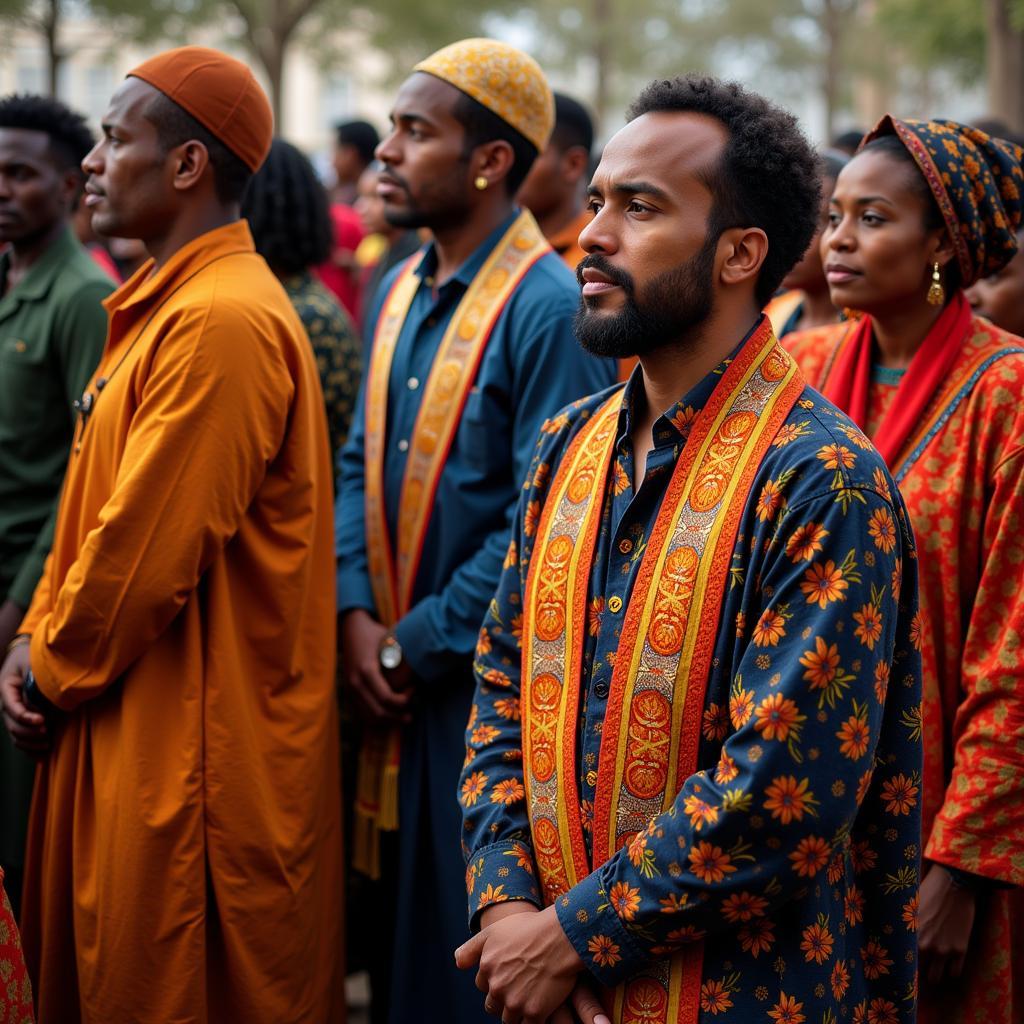 African Israelite Tribe Members During a Religious Ceremony
African Israelite Tribe Members During a Religious Ceremony
Tracing the Roots: Origins and Diaspora
The origins of African Israelite tribes are varied and often shrouded in oral history and ancestral narratives. Some communities trace their lineage back to ancient Jewish traders and migrants who settled in various parts of Africa over centuries. Others connect their heritage to the Beta Israel of Ethiopia, who have a long and documented history of practicing Judaism.
The transatlantic slave trade also played a role in shaping the development of African Israelite communities. Enslaved Africans brought with them their own spiritual beliefs and practices, which sometimes intertwined with elements of Judaism encountered in the Americas.
Diverse Expressions: From Ghana to South Africa
African Israelite tribes are not a monolithic group but rather a diverse collection of communities with their own unique interpretations of faith and identity. In Ghana, the House of Israel community observes Shabbat, practices circumcision, and adheres to dietary laws.
South Africa is home to a number of African Israelite groups, including the Lemba people, who have long claimed Jewish ancestry. Genetic studies have shown a possible link between the Lemba and the Cohenim, a priestly lineage within Judaism.
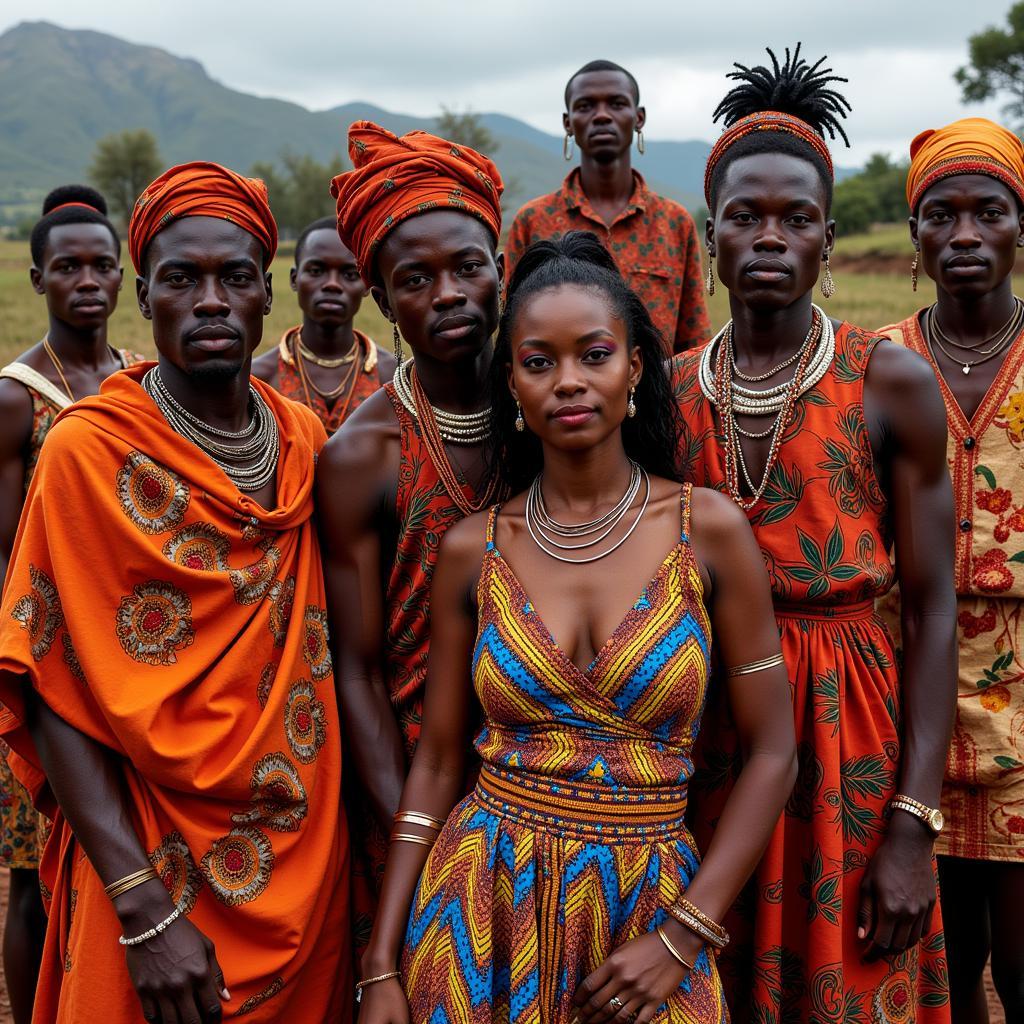 Lemba People in Traditional Attire
Lemba People in Traditional Attire
Cultural Practices and Beliefs
While specific practices vary widely, many African Israelite tribes share certain commonalities. These often include:
- Observance of the Sabbath: Resting from work and engaging in prayer and reflection on Saturdays.
- Dietary Laws: Following kosher-like dietary restrictions, such as abstaining from pork and shellfish.
- Circumcision: Practicing male circumcision as a ritual of faith.
- Reverence for the Torah: Recognizing the Hebrew Bible as a sacred text.
Navigating Identity: Challenges and Affirmation
African Israelite tribes often navigate complex societal landscapes. They may face questions about their claims of Israelite descent or encounter prejudice and discrimination based on their religious beliefs.
Despite these challenges, African Israelite communities continue to thrive, celebrating their unique cultural and religious heritage. They often play active roles in their local communities, contributing to social and economic development.
Looking Forward: Preservation and Evolution
As African Israelite tribes look to the future, they face the ongoing challenge of preserving their traditions while also adapting to a changing world. Many communities are actively engaged in educating younger generations about their history and beliefs, ensuring the continuity of their cultural practices.
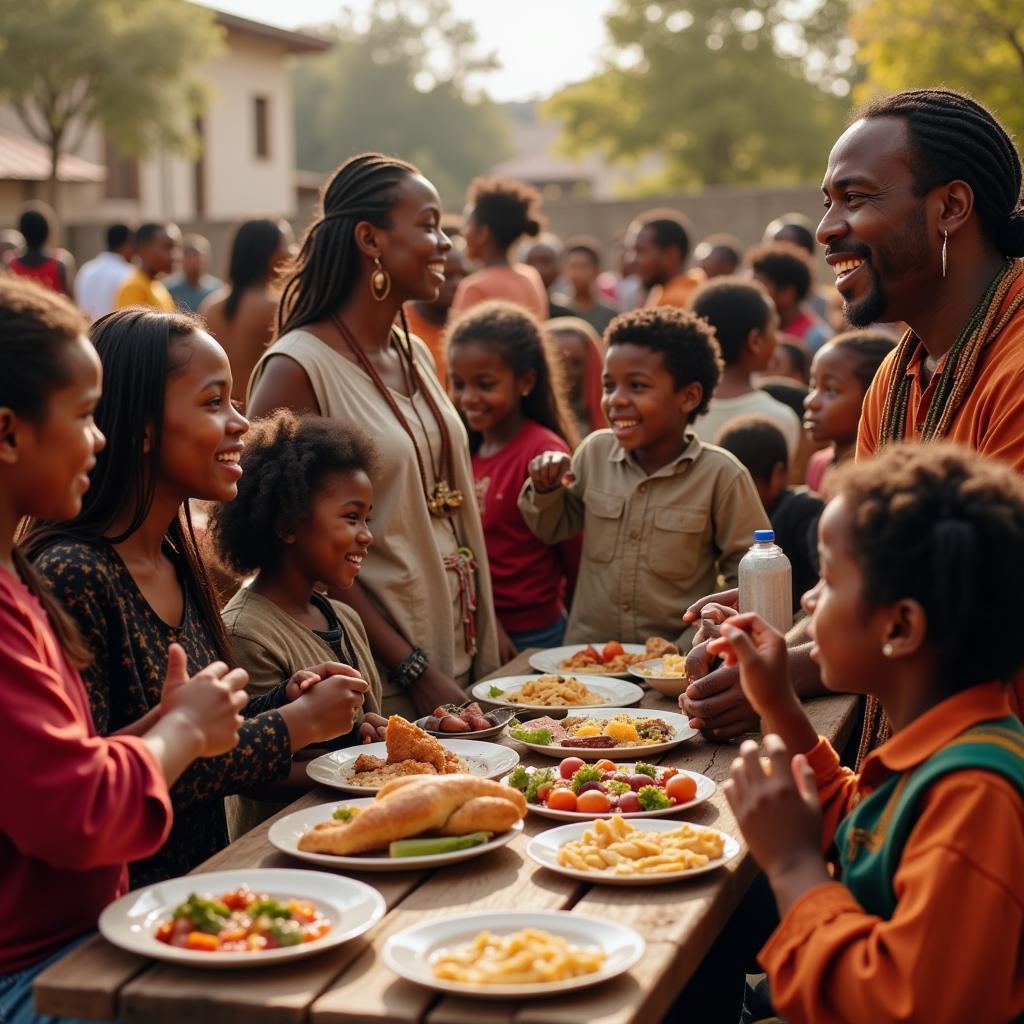 Members of an African Israelite Community Gathering
Members of an African Israelite Community Gathering
The story of African Israelite tribes is a testament to the enduring power of faith, identity, and cultural resilience. These communities remind us that the tapestry of human experience is rich and multifaceted, filled with diverse expressions of belief and belonging.
Conclusion
African Israelite tribes offer a captivating glimpse into the intersection of faith, culture, and identity on the African continent. Their stories challenge conventional understandings of Jewish history and diaspora while highlighting the dynamism and fluidity of religious expression. As these communities continue to evolve, they serve as a reminder of the importance of respecting and appreciating the diverse tapestry of human belief and cultural heritage.


