African Jungle Cheetah in Herds: Myth vs. Reality
The captivating image of African jungle cheetahs roaming in herds often sparks curiosity. While the idea of these sleek predators hunting together is intriguing, the reality of cheetah social structure is more nuanced. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of cheetah behavior and explore the truth behind their social dynamics.
Decoding Cheetah Social Structures: Beyond the Herd Mentality
Cheetahs are not typically herd animals like zebras or wildebeest. Their social structure is more complex and varies depending on age, sex, and family ties. Adult females are generally solitary, raising their cubs independently. However, these independent females aren’t entirely isolated. about african wildlife They maintain territories and may occasionally interact with other females, especially relatives.
The Coalition: Brothers in Arms
Male cheetahs, on the other hand, often form coalitions, typically consisting of brothers from the same litter. These coalitions work together to defend a territory and increase their chances of mating. The cooperative nature of coalitions allows them to take down larger prey and fend off rivals.
Mothers and Cubs: A Temporary Herd
Mother cheetahs with cubs represent another form of cheetah grouping. The mother fiercely protects her cubs, teaching them essential survival skills like hunting and avoiding predators. This family unit remains together until the cubs are old enough to fend for themselves, usually around 18 months.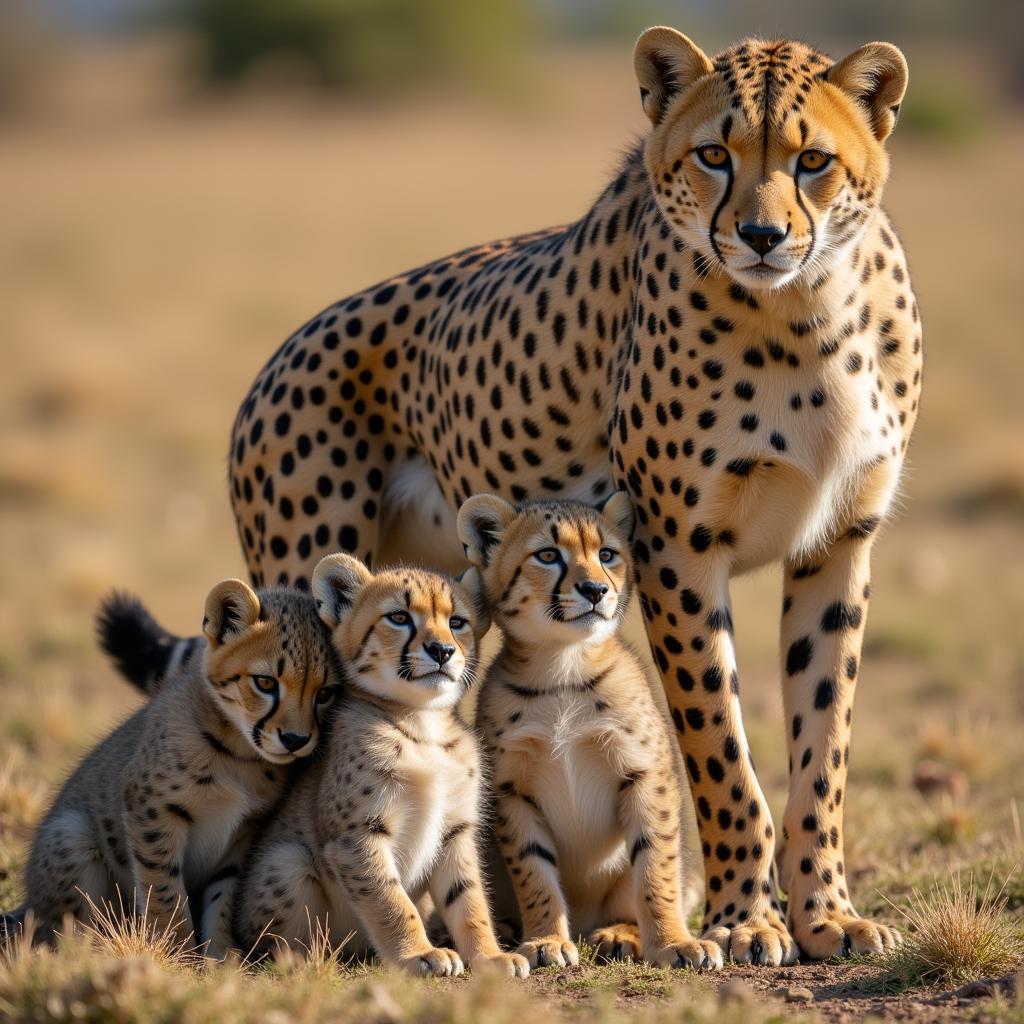  A cheetah mother guards her cubs from potential threats in the African savanna.
A cheetah mother guards her cubs from potential threats in the African savanna.
Do Cheetahs Ever Form Larger Groups?
While the term “herd” isn’t accurate for cheetahs, there can be instances where several individuals are observed in close proximity, especially around abundant food sources. However, these gatherings are usually temporary and don’t represent a stable social structure. african big game animals “It’s important to remember that cheetahs are adapted for speed and agility, not for cooperative hunting like lions,” explains Dr. Zara Hassan, a wildlife biologist specializing in cheetah behavior. “Their solitary nature reflects their hunting strategy, which focuses on short bursts of speed to ambush prey.”
The Myth of the Cheetah Herd
The idea of cheetahs hunting in large groups is a common misconception. Their slender build and reliance on speed make them less suited for coordinated hunts. Instead, they rely on stealth and rapid acceleration to capture their prey. “Cheetahs are masters of individual pursuit,” adds Dr. Hassan, “their hunting style is a testament to their incredible athleticism.”
Understanding Cheetah Behavior: Key Takeaways
- Cheetahs are not herd animals.
- Adult females are primarily solitary, except when raising cubs.
- Male cheetahs form coalitions, usually with brothers.
- Mothers and cubs form temporary family units.
- Large cheetah gatherings are rare and usually temporary.
Are Cheetahs Social Animals?
While not herd animals, cheetahs do exhibit social behaviors, particularly within coalitions and family units. These social interactions play a vital role in their survival and reproductive success.
The Solitary Hunter: A Strategy for Success
The solitary nature of cheetahs is a crucial adaptation for their hunting style. Their speed and agility allow them to pursue prey individually, maximizing their chances of a successful kill.
In conclusion, the image of African jungle cheetahs in herds is largely a myth. Their social structure is complex and dynamic, encompassing solitary females, male coalitions, and temporary family units. Understanding these nuanced social behaviors is crucial for appreciating the fascinating world of these magnificent predators. african birth animal by month Learning the truth behind cheetah social dynamics allows us to dispel myths and appreciate their unique adaptations for survival.
FAQ
- What is a cheetah coalition? A group of male cheetahs, usually brothers, that work together.
- How long do cheetah mothers stay with their cubs? Around 18 months.
- Why are cheetahs not considered herd animals? Their social structure is based on smaller, more specific groups.
- What is the primary hunting strategy of cheetahs? Solitary pursuit and ambush.
- Do cheetahs hunt cooperatively? Rarely, they primarily hunt alone.
- What are the different cheetah social groups? Solitary females, male coalitions, and mother-cub families.
- How do cheetah coalitions benefit males? Improved territory defense and mating opportunities.
You might also be interested in:
- African Elephant Facts and Information
african elephant facts and information
When you need assistance, please contact us at Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. We have a 24/7 customer service team.