African Killer Bees vs Honey Bees: A Stinging Comparison
African killer bees and honey bees are often confused, but there are some key differences between these two types of bees. Understanding these differences can be particularly important if you live in an area where both types of bees are present.
Origins and Spread: The Tale of Two Bees
While both share ancestry from the European honey bee, their paths diverged dramatically.
-
Honey bees, originally from Europe, were introduced to North America by colonists centuries ago. These bees are renowned for their honey production and pollination prowess.
-
Africanized honey bees, more commonly known as African killer bees, have a more dramatic origin story. In the 1950s, scientists in Brazil crossed African honey bees with European honey bees with the goal of improving honey production in tropical climates. Unfortunately, some of these hybrid bees escaped quarantine and began breeding with local populations, leading to the spread of Africanized honey bees throughout South and North America.
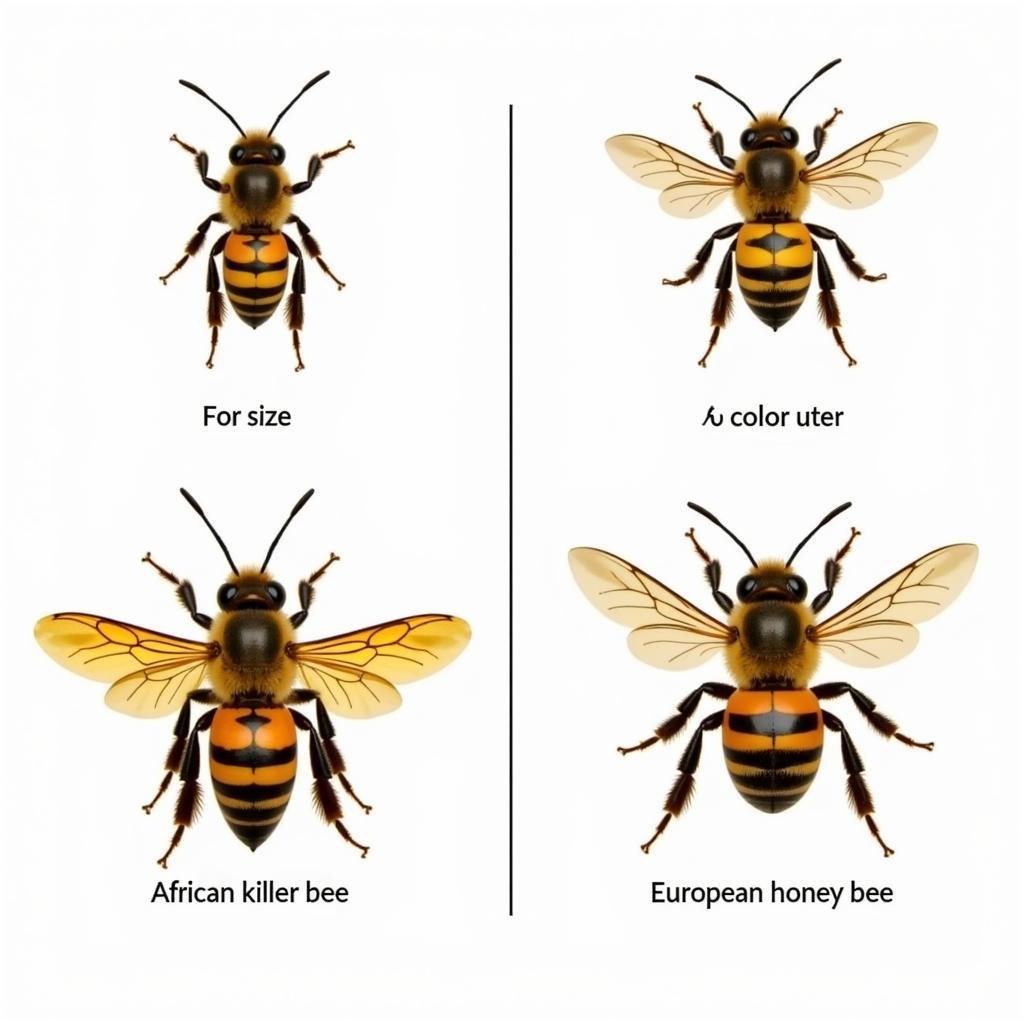 African Killer Bee and European Honey Bee Comparison
African Killer Bee and European Honey Bee Comparison
Appearance: Spotting the Subtle Differences
Telling these bees apart by sight alone can be tricky for the untrained eye.
-
African killer bees are slightly smaller than their European counterparts, making visual identification difficult.
-
Honey bees are typically a shade darker, but this difference is often too subtle to be a reliable way to tell them apart.
Behavior: The Sting in the Tale
This is where the differences become critical. While both species will defend their hives, Africanized bees are far more aggressive and react more quickly to disturbances.
-
African killer bees defend a larger area around their hive and respond to perceived threats with greater numbers. Their stings are no more venomous than a honey bee’s, but their increased aggression makes them a significant danger.
-
Honey bees are generally docile and will only sting when threatened directly or when defending their hive.
Impact on Humans and the Environment
Understanding the behavioral differences between these bees is crucial for safety and ecological balance.
-
African killer bees pose a greater risk to humans and animals due to their heightened defensive behavior. Their presence can disrupt outdoor activities and necessitate extra precautions in areas where they are common.
-
Honey bees, being more docile and essential pollinators, play a vital role in agriculture and ecosystem health.
What to Do When Encountering Africanized Bees
If you find yourself facing an aggressive swarm, remember these safety tips:
-
Run: Quickly move away from the area. Don’t try to swat at the bees or hide in water as they will wait for you to resurface.
-
Seek Shelter: Find a car, building, or other enclosed space as quickly as possible.
-
Cover Your Face and Head: Protect your face and head as these are the areas most likely to be targeted by the bees.
-
Do Not Swat: Swatting will only agitate the bees further.
-
Call for Help: Once you are safely away, contact local authorities or pest control professionals to handle the situation.
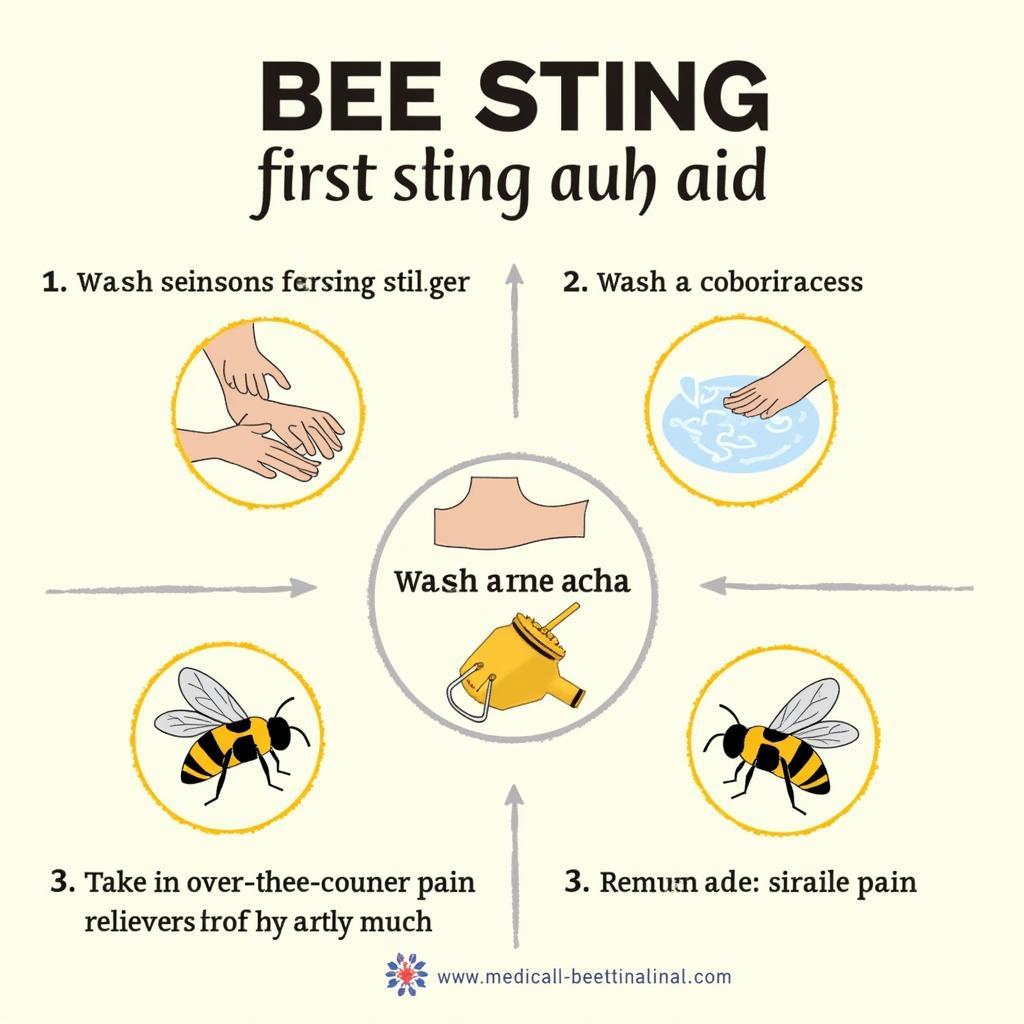 Bee Sting First Aid
Bee Sting First Aid
Living in Coexistence: Respect and Awareness
While African killer bees present real challenges, understanding their behavior and taking appropriate precautions can mitigate risks. Respecting their space, being vigilant in areas where they are common, and promoting awareness are key to peaceful coexistence.


