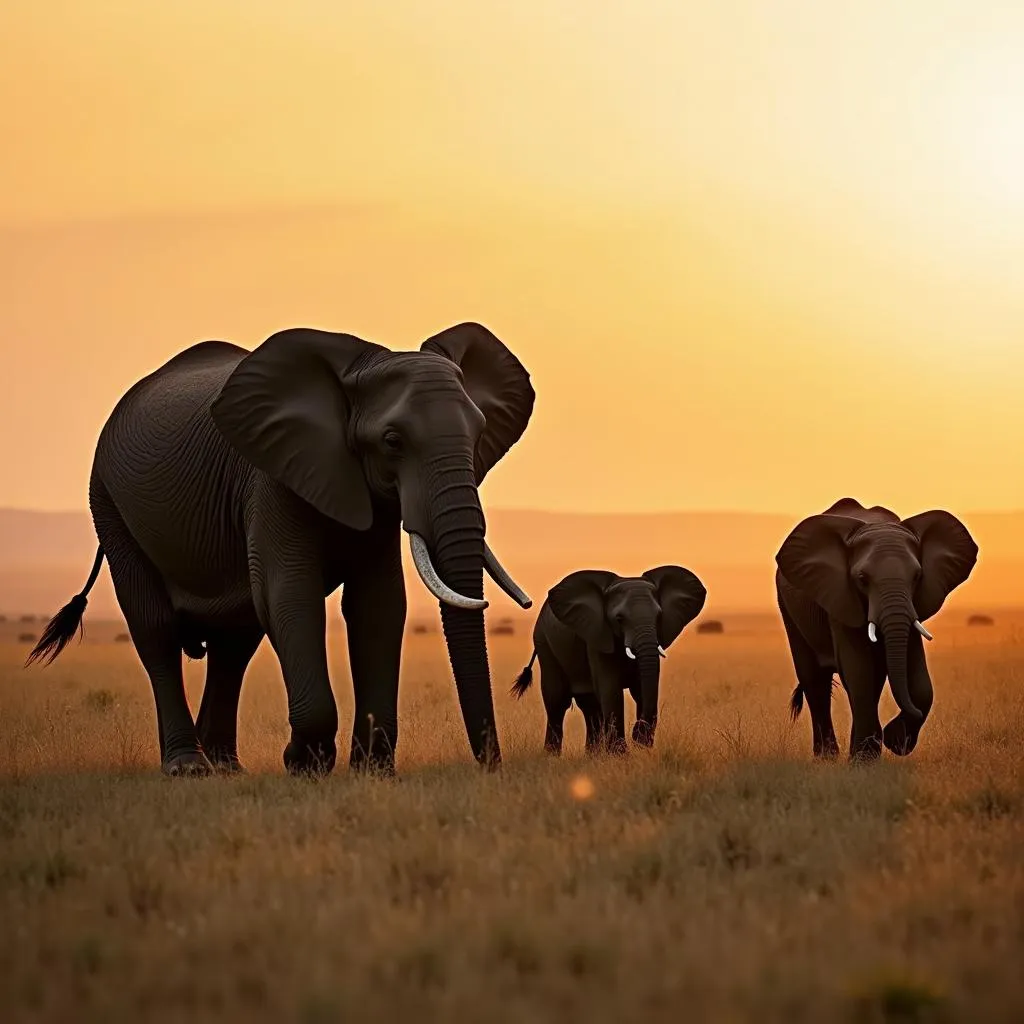
The Adorable Baby African Elephant: A Gentle Giant in the Making
Baby African Elephants, with their oversized ears and playful trunks, are undeniably captivating. These miniature giants represent the future of Africa’s savannas and forests, embodying both vulnerability and the promise of enduring strength. From their first wobbly steps to their heartwarming interactions with their family herds, baby elephants offer a unique glimpse into the complex social dynamics and fascinating lives of these intelligent creatures. Let’s delve into the world of these adorable baby African elephants.
Understanding the Baby African Elephant: Size, Diet, and Development
A newborn baby African elephant, also known as a calf, typically weighs between 200 and 260 pounds and stands about three feet tall. These newborns, though small compared to their adult counterparts, are still quite sizable! Their diet consists solely of their mother’s milk for the first few months, providing them with essential nutrients for rapid growth and development. As they grow older, they gradually begin to explore solid foods, mimicking the foraging behavior of the adults in their herd. This learning process is crucial, equipping them with the skills necessary for survival in the wild.
The African bush elephant baby and the African forest elephant baby have slight differences, primarily in size and habitat. For instance, the forest elephant calf is slightly smaller than the bush elephant calf. These adaptations reflect the unique challenges and opportunities presented by their respective environments.
After a few paragraphs, it’s worthwhile to explore the weight of a baby African bush elephant in more detail. You can find more information about the African bush elephant baby weight here.
The Importance of Family: Social Bonds and Protection
Baby African elephants are highly social animals, relying heavily on the protection and guidance of their family herd. The herd, led by a matriarch (the oldest and most experienced female), provides a safe and nurturing environment for the calves to grow and learn. The matriarch plays a vital role in teaching the young elephants essential survival skills, such as finding food and water, navigating the terrain, and recognizing potential dangers. Other female elephants in the herd, often relatives of the calf, also contribute to its upbringing, acting as “alloparents” or surrogate mothers. This cooperative childcare system ensures the calf’s well-being and maximizes its chances of survival. Learn more about African Bush Elephant Baby here.
Threats and Conservation Efforts for Baby African Elephants
Sadly, baby African elephants face numerous threats, primarily due to human activities. Habitat loss due to deforestation and expanding human settlements reduces their access to food and water, forcing them into closer proximity with humans, leading to increased conflict. Poaching for ivory remains a significant threat, devastating elephant populations and leaving many calves orphaned. Understanding the difference between African elephant baby vs Indian elephant baby can be helpful in conservation efforts.
Fortunately, numerous organizations are dedicated to protecting these magnificent creatures. Conservation efforts focus on combating poaching, protecting elephant habitats, and raising awareness about the importance of elephant conservation. These initiatives are crucial for ensuring the survival of baby African elephants and the future of these iconic animals.
Curious to learn more? Discover the African forest elephant baby and its unique adaptations.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Future for Baby African Elephants
Baby African elephants are a symbol of hope for the future of Africa’s wildlife. By supporting conservation efforts and raising awareness about the threats they face, we can help ensure that these gentle giants continue to roam the African savannas and forests for generations to come. Protecting baby African elephants is not just about preserving a species; it’s about safeguarding the biodiversity of our planet and ensuring a future where these magnificent creatures can thrive. Learn more about African elephant baby elephant baby.
FAQs
-
What do baby African elephants eat?
- Baby African elephants primarily drink their mother’s milk for the first few years, gradually transitioning to solid food.
-
How long do baby African elephants stay with their mothers?
- Baby African elephants stay with their mothers and the herd for several years, learning essential survival skills.
-
What are the biggest threats to baby African elephants?
- The biggest threats include habitat loss and poaching.
-
How can I help protect baby African elephants?
- You can support conservation organizations, spread awareness, and advocate for policies that protect elephants.
-
What is the role of the matriarch in an elephant herd?
- The matriarch leads the herd, provides guidance, and teaches young elephants essential survival skills.
Situations involving questions about baby elephants
- Tourist on safari: A tourist might ask their guide about the age of a baby elephant they spot, or how to differentiate between a baby and a juvenile.
- Student researching elephants: A student might be looking for information on the social behavior of baby elephants and their interactions within the herd.
- Concerned citizen: A concerned individual may inquire about the threats facing baby elephants and ways to contribute to conservation efforts.
Other questions and related articles:
- How long do African elephants live?
- What is the difference between African and Asian elephants?
- The impact of climate change on African elephant populations
Need help? Contact us 24/7: Phone: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com Or visit us at: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.