Difference Between African Elephant and Asian Elephant
African and Asian elephants, while both majestic creatures, possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. This article delves into the key differences between these two iconic species, exploring their physical attributes, habitats, behaviors, and conservation status. We’ll uncover the fascinating nuances that make each elephant unique, highlighting the importance of understanding and protecting these magnificent animals.
African elephants are generally larger than their Asian counterparts, boasting larger ears shaped like the African continent. They also have more wrinkled skin and both males and females can grow tusks. Asian elephants, on the other hand, have smaller, rounded ears and smoother skin, with tusks typically only present in males. The differences extend beyond their appearance, encompassing their diets, social structures, and even the shape of their backs. Let’s take a closer look at the specifics that distinguish these two remarkable species.
Physical Distinctions: A Tale of Two Trunks
Perhaps the most noticeable difference lies in their ears. African elephants have large, fan-shaped ears that resemble the outline of Africa, while Asian elephants have smaller, rounded ears. This difference in ear size serves a practical purpose: African elephants use their large ears to dissipate heat in the hot African savanna, while Asian elephants, living in cooler, forested environments, don’t require such extensive heat regulation. Another key differentiator is the shape of their backs. African elephants have a concave back, while Asian elephants have a convex or level back.
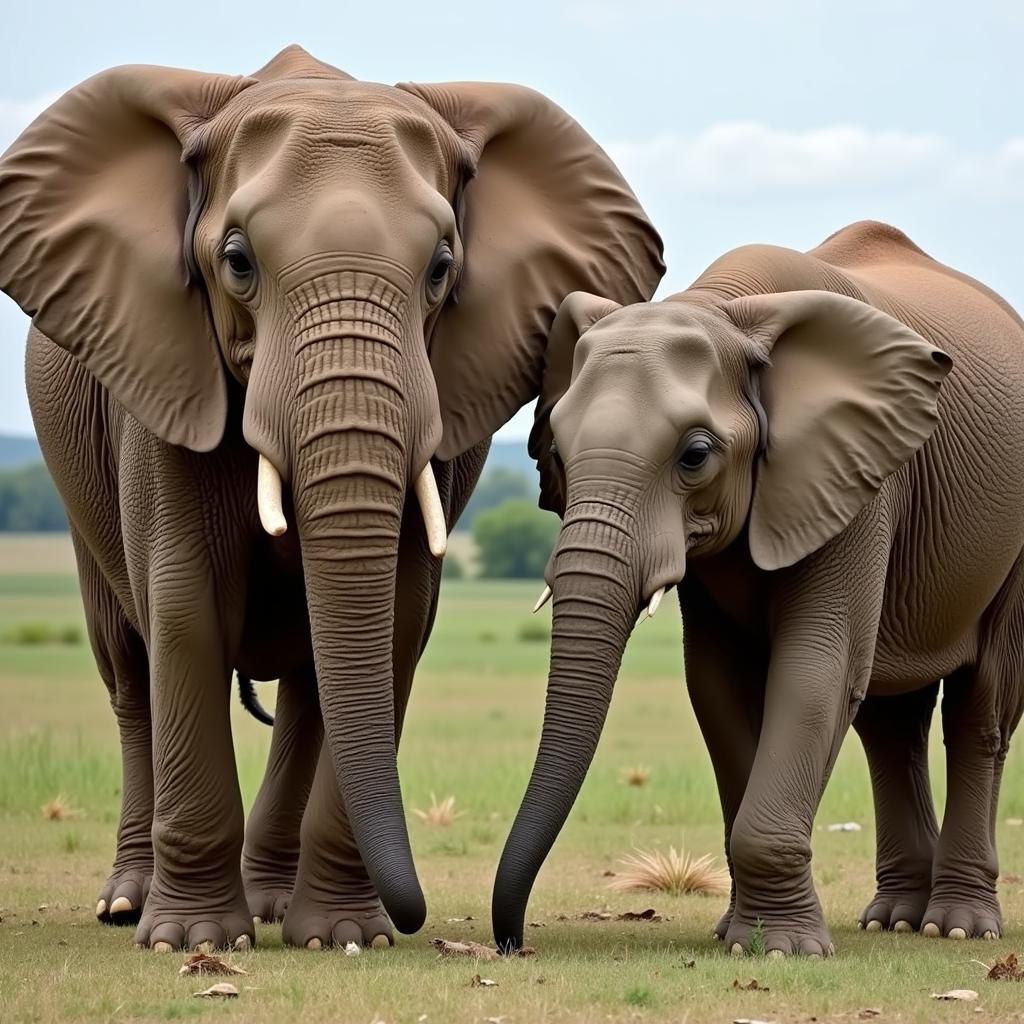 African and Asian Elephant Ear Comparison
African and Asian Elephant Ear Comparison
Furthermore, the tips of their trunks also differ. African elephants have two “fingers” at the tip of their trunk, used for grasping and manipulating objects, while Asian elephants have only one. This seemingly small difference plays a significant role in how they interact with their surroundings. African elephants use their two-fingered trunk to pluck leaves and branches, while Asian elephants, with their single-fingered trunk, are more adept at curling and picking up smaller objects.
Habitat and Distribution: From Savanna to Rainforest
Where these elephants live tells us a lot about their adaptations. African elephants are found across sub-Saharan Africa, inhabiting a variety of environments from savannas and grasslands to forests and deserts. The African elephant endangered article provides further insights into their conservation status. Asian elephants, meanwhile, are found in the forests and grasslands of India, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia. This difference in habitat directly influences their dietary habits and social structures.
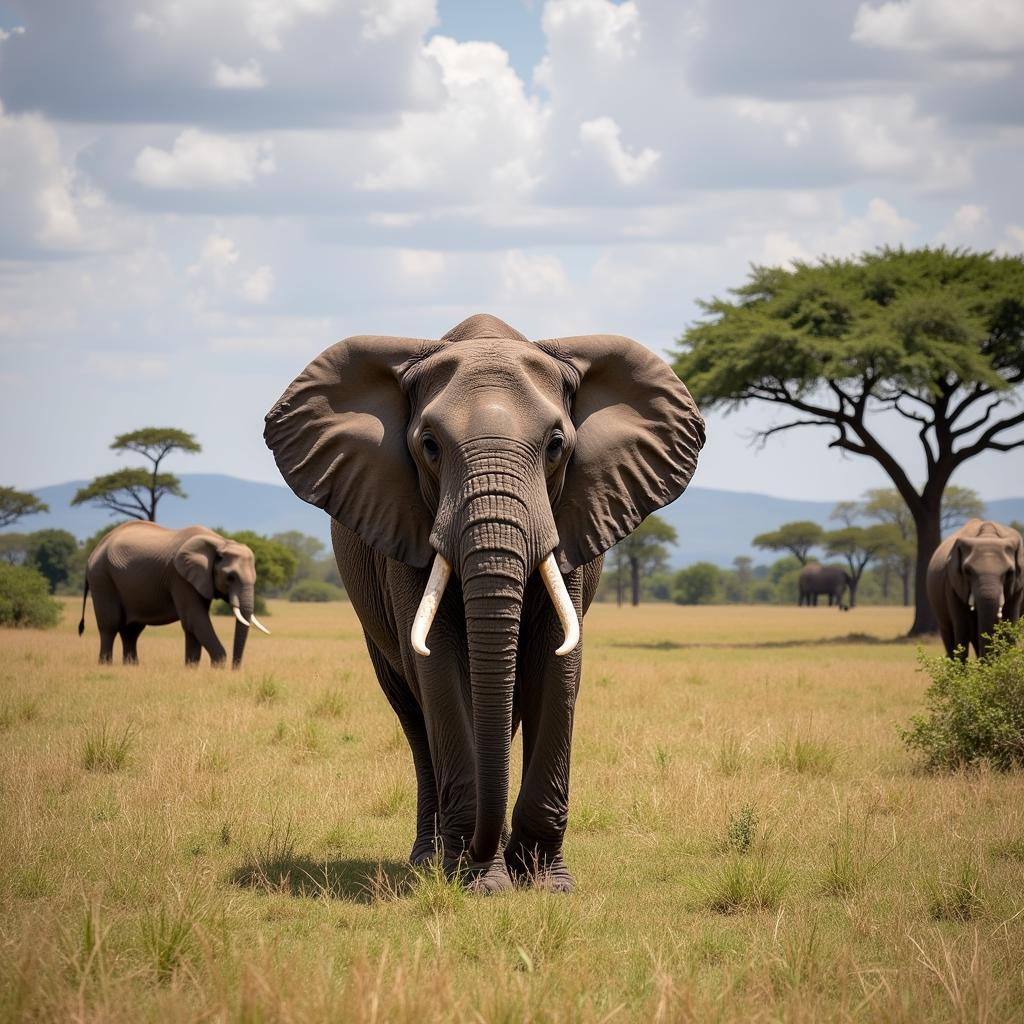 African Elephant in Savanna Habitat
African Elephant in Savanna Habitat
The article on the African chromosome provides additional information on their genetic makeup and how it relates to their adaptability to diverse habitats.
Behavior and Social Structure: Family Ties and Herd Dynamics
Both African and Asian elephants are highly social animals, living in complex herd structures. However, there are subtle differences in their social dynamics. African elephant herds are typically led by a matriarch, the oldest and most experienced female, who guides the herd in their search for food and water. Asian elephant herds are often smaller and less structured than their African counterparts. Check out the African elephant AR experience for an interactive look at these social structures.
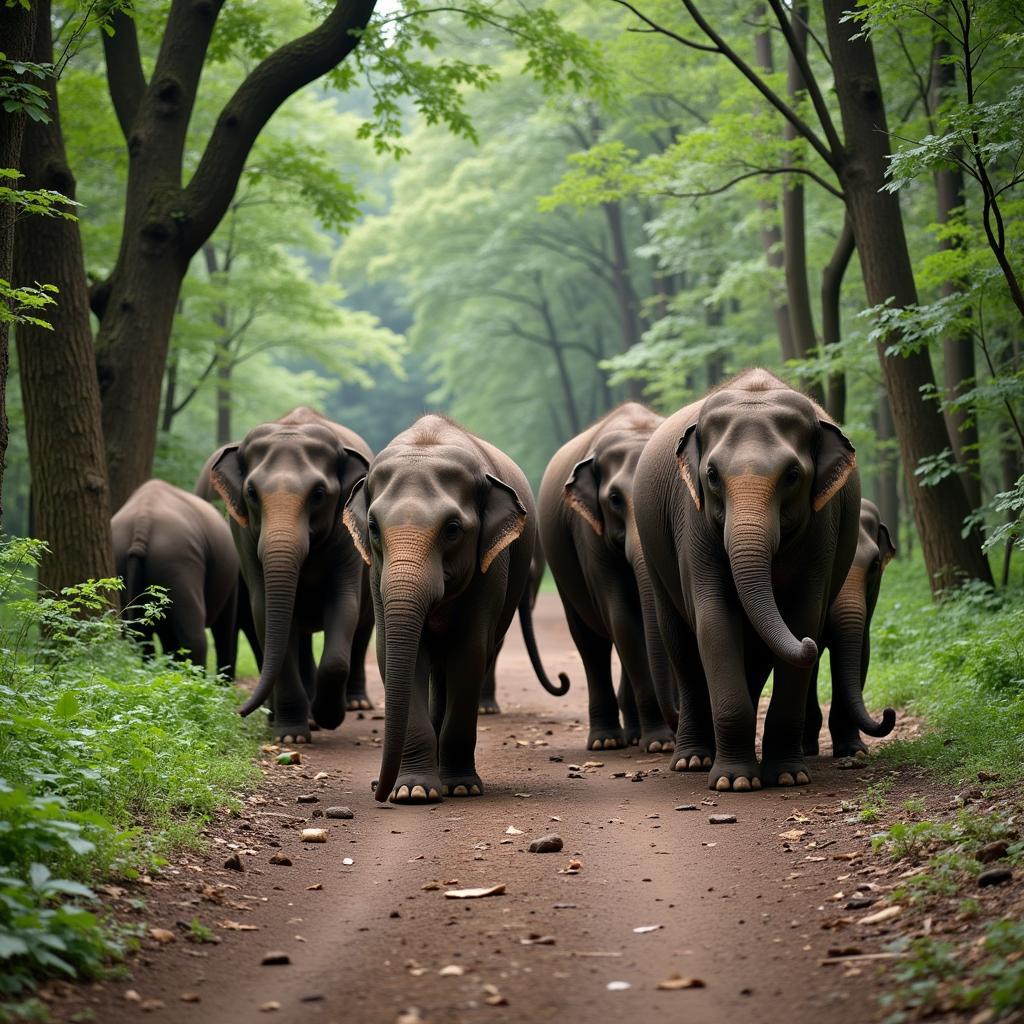 Asian Elephant Herd in Forest
Asian Elephant Herd in Forest
Conservation Challenges: Protecting Giants Under Threat
Both African and Asian elephants face significant conservation challenges. Poaching for ivory, habitat loss due to deforestation and human encroachment, and human-wildlife conflict are major threats to both species. Understanding the specific challenges faced by each species is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. For instance, the unique genetic makeup of African elephants, as explored in the resource on the African chromosome, plays a crucial role in their conservation.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Diversity of Elephants
African and Asian elephants, while sharing a common ancestry, have evolved distinct characteristics that reflect their unique environments and lifestyles. From their physical attributes to their social behaviors, these differences highlight the incredible diversity of the elephant family. Understanding these differences is not only fascinating but also essential for the conservation of these magnificent creatures. By appreciating the unique qualities of each species, we can better protect them for future generations. The Difference Between African Elephant And Asian Elephant underscores the importance of tailored conservation efforts for each species.
FAQ
- What’s the main difference in the ears of African and Asian elephants? African elephants have large, fan-shaped ears, while Asian elephants have smaller, rounded ears.
- Do both male and female African elephants have tusks? Yes, unlike Asian elephants where primarily males have tusks.
- Where do Asian elephants primarily live? Asian elephants live in the forests and grasslands of India, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia.
- What is the shape of an African elephant’s back? African elephants have a concave, dipped back.
- How many “fingers” does an African elephant have at the tip of its trunk? Two, while Asian elephants have one.
- What are the main threats to both African and Asian elephants? Poaching, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict.
- Why is understanding the difference between these two species important? It’s crucial for developing effective, species-specific conservation strategies.
Further Exploration
Consider exploring related articles such as “African Elephant Head Black and White” and “African Elephant in India” for more in-depth information on these magnificent creatures.
Need Help?
For any assistance or inquiries, please contact us:
Phone: +255768904061,
Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com
Address: Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania.
Our customer service team is available 24/7.