Languages Spoken in African Countries: A Diverse Linguistic Landscape
Africa is a continent renowned for its rich cultural tapestry, and a key thread in this tapestry is the incredible diversity of Languages Spoken In African Countries. With an estimated 2,000 languages, representing roughly one-third of the world’s total, Africa boasts a linguistic landscape as varied as its geography and people. This article delves into the fascinating world of African languages, exploring their origins, classifications, and impact on the continent’s cultural identity.
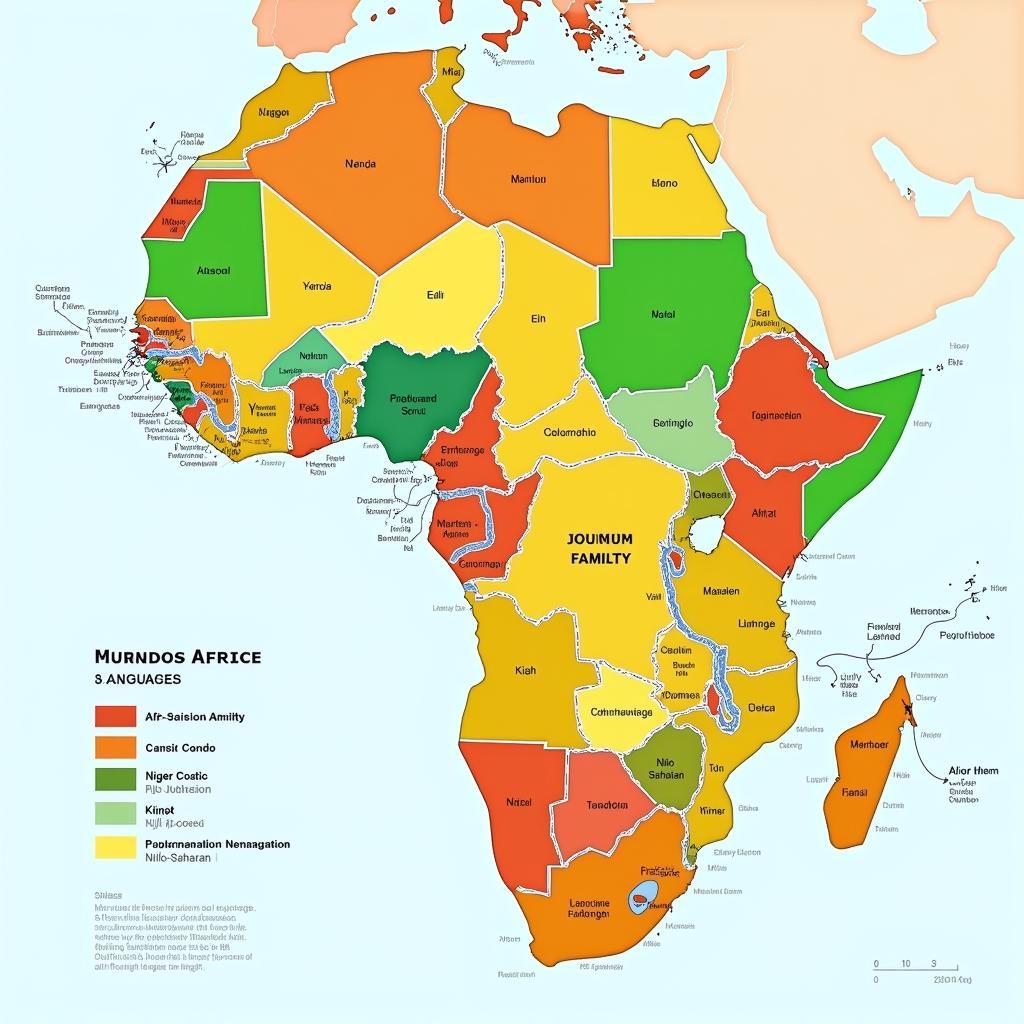 Map of Diverse African Languages Across the Continent
Map of Diverse African Languages Across the Continent
Exploring the Major Language Families of Africa
The languages spoken in African countries are categorized into four main families: Afro-Asiatic, Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan, and Khoisan. The Afro-Asiatic family, prominent in North Africa, includes languages like Arabic, Berber, and Somali. The Niger-Congo family, the largest in Africa, encompasses Bantu languages such as Swahili, Zulu, and Xhosa, which are spoken across Sub-Saharan Africa. The Nilo-Saharan family, found in parts of East and Central Africa, includes languages like Maasai and Luo. Finally, the Khoisan languages, primarily spoken in Southern Africa, are known for their unique click consonants. These language families further branch into numerous subfamilies and individual languages, reflecting the intricate linguistic history of the continent.
Did you know that Swahili, a Bantu language, is one of the most widely spoken languages in Africa, serving as a lingua franca in East Africa? It facilitates communication between people from different ethnic backgrounds.
The Influence of Colonization on Languages Spoken in African Countries
The colonial era significantly impacted the languages spoken in African countries. European languages, such as English, French, Portuguese, and Spanish, were imposed as official languages in many African nations. This led to the marginalization of indigenous African languages in education, government, and other formal settings. However, African languages continued to thrive in everyday communication, playing a vital role in preserving cultural traditions and identities. Many African countries now recognize the importance of promoting their indigenous languages alongside official European languages. You might be surprised to learn that many African countries have adopted multilingual policies, promoting both indigenous and European languages.
Beyond the Official Languages: A Tapestry of Dialects
While official languages are crucial for national unity and administration, the linguistic landscape of Africa extends far beyond these designated tongues. A multitude of dialects exist within each language group, enriching the tapestry of communication across the continent. These dialects often reflect regional variations, cultural nuances, and historical influences, adding another layer of complexity to the already diverse linguistic environment.
How Many Languages are Spoken in South Africa?
South Africa, known for its linguistic diversity, recognizes 11 official languages, reflecting the country’s multicultural heritage. These languages include Zulu, Xhosa, Afrikaans, English, and several others. Want to explore South Africa further? Check out 5 south african countries. Learning about the numerous dialects spoken within these languages provides a deeper understanding of the cultural richness and linguistic complexity of South Africa. For those interested in African American linguistic history, african american language history provides valuable insights.
Preserving and Promoting African Languages in a Globalized World
In an increasingly globalized world, the preservation and promotion of African languages face numerous challenges. Language endangerment is a pressing concern, as some languages are at risk of extinction due to factors like urbanization and the dominance of global languages. However, efforts are underway to revitalize endangered languages, through language documentation projects, community-based language programs, and the integration of African languages into education systems. For a unique African travel experience, consider african breeze safaris. If you are interested in career opportunities in Africa, african country any available planning engineer job may provide some leads. For a blend of African and other cultures, explore african culture in mauritius. Dr. Abimbola Adisa, a renowned linguist specializing in African languages, emphasizes the importance of language preservation, stating, “African languages are not just tools of communication; they are repositories of knowledge, culture, and history.” Another expert, Professor Nana Ama Asamoah, adds, “Investing in language preservation is investing in the future of Africa.”
In conclusion, the languages spoken in African countries represent a vital part of the continent’s heritage. From the widely spoken languages like Swahili and Arabic to the endangered languages facing extinction, each language contributes to the rich tapestry of African culture and identity. By understanding and appreciating the diversity of languages spoken in African countries, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s vibrant cultural landscape.
FAQ
-
What is the most spoken language in Africa? While various languages hold significant regional importance, Arabic, Swahili, French, English, and Hausa are among the most widely spoken across different parts of the continent.
-
How many language families are there in Africa? There are four main language families: Afro-Asiatic, Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan, and Khoisan.
-
Why are some African languages endangered? Factors such as urbanization, globalization, and the dominance of official languages contribute to the endangerment of some African languages.
-
What is being done to preserve African languages? Efforts include language documentation projects, community-based language programs, and integrating African languages into education.
-
Why is it important to preserve African languages? African languages are not merely communication tools; they are repositories of cultural knowledge, traditions, and history.
For further assistance, please contact us at Phone Number: +255768904061, Email: kaka.mag@gmail.com, or visit us at Mbarali DC Mawindi, Kangaga, Tanzania. Our customer service team is available 24/7.



